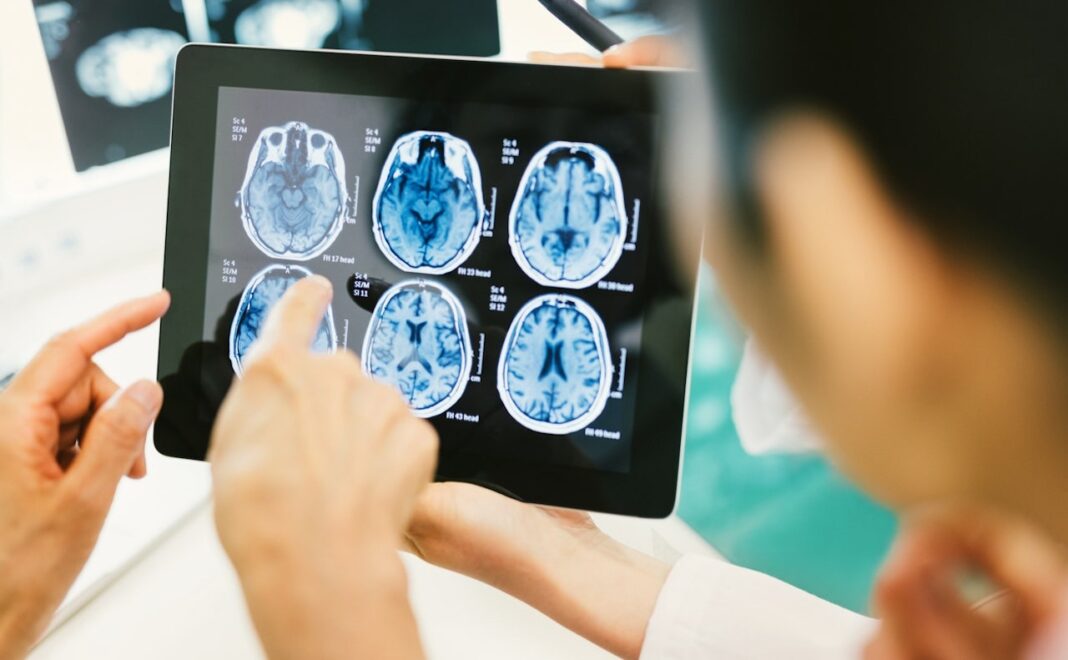
New particulars have emerged about how Alzheimer’s disease impacts the mind.
Researchers led by the Allen Institute for Mind Science in Seattle and College of Washington Medication have recognized mobile adjustments within the brains of individuals with the illness — and a timeline of after they happen.
“As a substitute of AD simply by way of the same old lens of plaques and tangles, we centered on how particular cell varieties have been modified in every section,” examine writer Dr. Kyle Travaglini, Ph.D., a scientist at Allen Institute, informed Fox Information Digital through e-mail.
ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE COULD BE SLOWED BY BOOSTING A CERTAIN PROTEIN IN THE BRAIN, RESEARCHERS SAY
“We recognized two primary phases in AD by arranging donors alongside a steady illness trajectory — a sluggish, early section with low ranges of pathology and no cognitive decline, adopted by a later section the place there’s an enormous buildup of pathology and cognitive decline.”

Researchers study donated mind tissue samples by way of a microscope in a lab on the Allen Institute. (Allen Institute for Mind Science)
The examine, which was printed this week in Nature Neuroscience, examined hundreds of thousands of cells from the donated mind tissue of 84 deceased Alzheimer’s sufferers.
The donors ranged from gentle instances with no signs to superior dementia instances.
TO REDUCE DEMENTIA RISK, SENIORS SHOULD TAKE UP THIS OUTDOOR ACTIVITY, STUDY SUGGESTS
“By finding out analysis topics throughout the spectrum of AD, together with these within the earliest phases of illness, we hope to determine susceptible cells early within the illness course of, lengthy earlier than an individual develops signs,” C. Dirk Keene, professor of neuropathology at UW Medication, mentioned in a press launch.
Researchers centered on the center temporal gyrus (MTG) — the a part of the mind that controls language, reminiscence and imaginative and prescient.
That portion of the mind is named a “vital transition zone,” the place proof of Alzheimer’s seems after which worsens because the illness progresses.
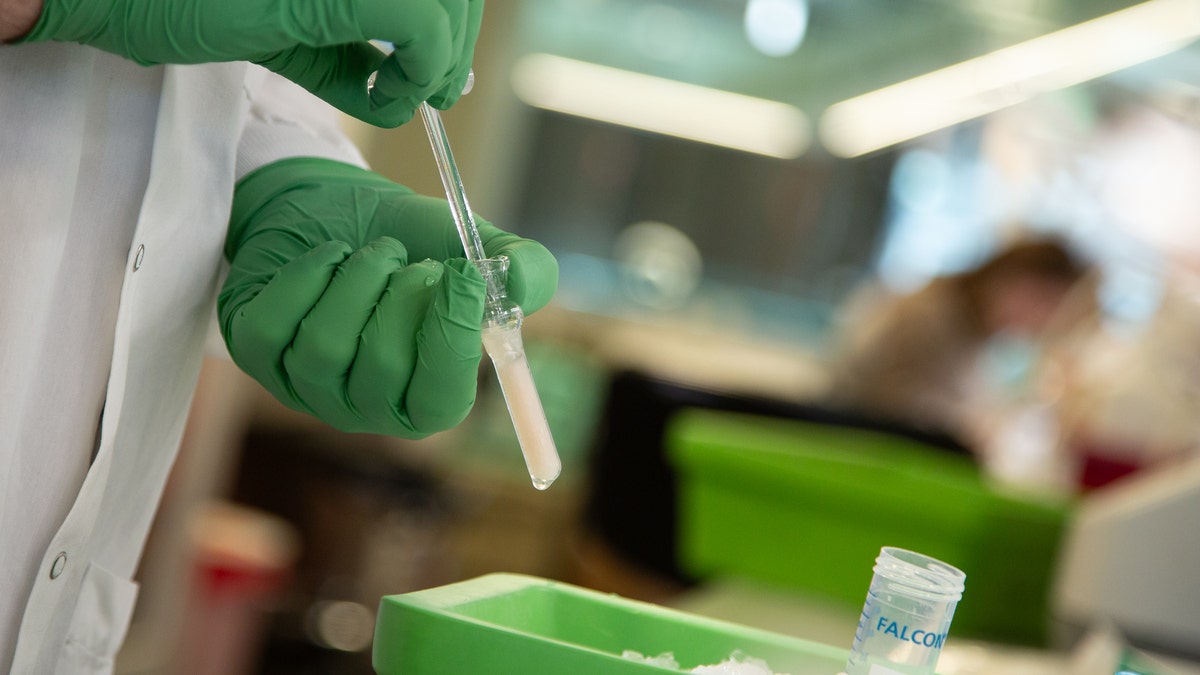
A scientist creates a pattern within the lab on the Allen Institute. (Allen Institute for Mind Science)
Utilizing machine studying expertise, researchers in contrast the cells, genes and DNA of the Alzheimer’s brain samples to maps of the conventional mind generated by the Allen Institute.
“With these instruments, scientists have been in a position to detect the earliest mobile adjustments to the mind to create a extra full image of what occurs over the complete course of the illness,” John Ngai, Ph.D., director of The BRAIN Initiative, mentioned within the launch.
“We created a pathology clock that tells not solely what adjustments are taking place on this cortical area, however when.”
“The brand new data offered by this examine could assist scientists and drug developers around the globe develop diagnostics and coverings focused to particular phases of Alzheimer’s and different dementias,” he added.
Making a illness timeline
The examine recognized “two distinct phases” of Alzheimer’s illness.
“You might say we created a pathology clock that tells not solely what adjustments are taking place on this cortical area, however when,” mentioned Mariano Gabitto, Ph.D., a lead writer and assistant investigator on the Allen Institute, within the launch.

Researchers examine photographs of mind tissue to find out Alzheimer’s-related mobile adjustments. (Allen Institute for Mind Science)
First, there was a “sluggish, early buildup of irregular mobile adjustments,” the researchers famous.
Throughout this era, the affected person could not expertise any signs of reminiscence loss or cognitive decline.
In that first section, the researchers have been shocked to find the lack of sure inhibitory neurons that weren’t beforehand linked to Alzheimer’s.
DEMENTIA ADVICE: HERE ARE 16 SAFE THINGS TO SAY TO YOUR LOVED ONE
Travaglini described that as a “vital discovery,” as these neurons act as “brakes” for mind exercise and “preserve issues balanced.”
“This specificity offers us new clues about how and why sure mind circuits might break down in AD,” he mentioned.

Researchers analyze mind tissue samples in a lab on the Allen Institute. (Allen Institute for Mind Science)
Richard J. Hodes, MD, director of the NIH Nationwide Institute on Getting old, famous that one of many challenges in diagnosing and treating Alzheimer’s is that a lot of the injury to the mind occurs on this early section, earlier than signs happen.
CLICK HERE TO GET THE FOX NEWS APP
“The power to detect these early adjustments signifies that, for the primary time, we will see what is going on to an individual’s mind through the earliest intervals of the illness,” he mentioned within the launch.
“For the primary time, we will see what is going on to an individual’s mind through the earliest intervals of the illness.”
The second section was marked by a “far more in depth loss” of various kinds of neurons and cells, resulting in the buildup of the hallmark “plaques and tangles” within the mind — which is often when sufferers start to note cognitive decline.
The larger image
Igor Camargo Fontana, Ph.D., Alzheimer’s Affiliation director of scientific convention programming in Chicago, was not concerned within the examine however shared what he described because the “greater image” it revealed.
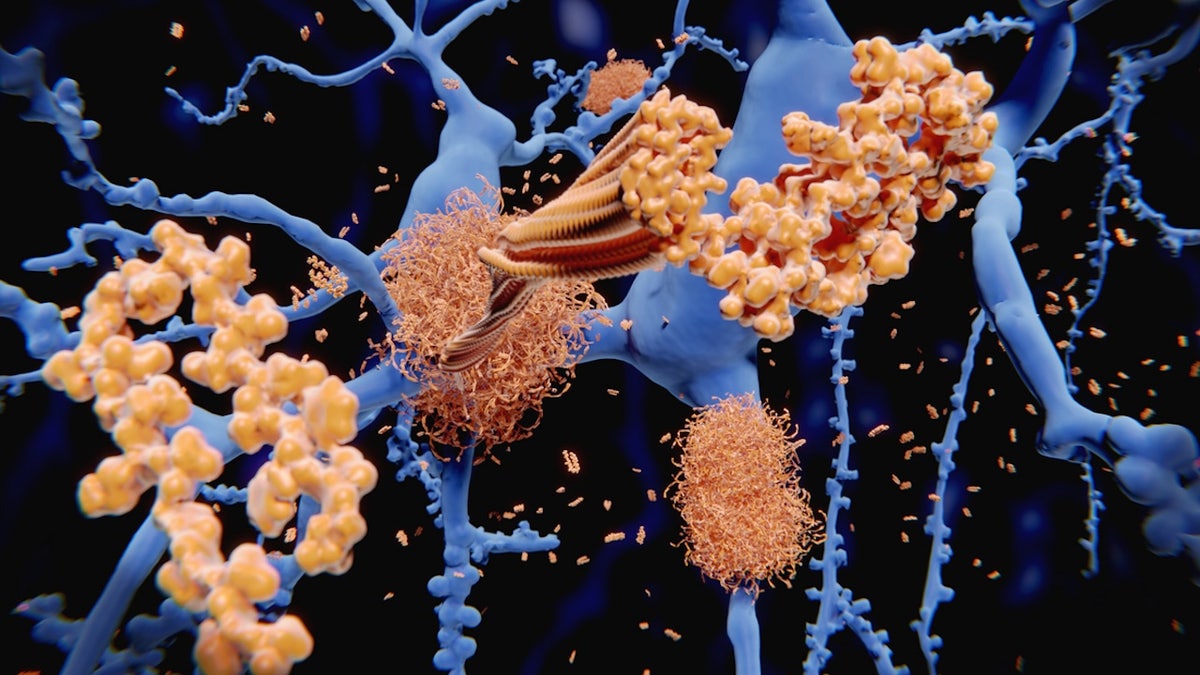
“As a substitute of AD simply by way of the same old lens of plaques and tangles, we centered on how particular cell varieties have been modified in every section,” a researcher mentioned. (iStock)
“Alzheimer’s illness has a protracted pre-symptomatic interval; Alzheimer’s-related adjustments happen within the mind 10, 15 and even 20 years earlier than the onset of reminiscence and pondering signs,” he informed Fox Information Digital.
CLICK HERE TO SIGN UP FOR OUR HEALTH NEWSLETTER
“If the findings on this new paper are confirmed by different labs, it raises the query of whether or not successfully addressing the mind adjustments that occur in what the authors name the primary ‘quiet’ section can sluggish, delay or forestall the second, extra damaging section.”
The hope is that this new timeline of how the illness impacts the mind will assist information the event of latest remedies. (iStock)
Wanting forward, Fontana says it is going to be necessary to additional examine the “quiet” section to substantiate the way it’s linked to the better-known biomarkers of Alzheimer’s, similar to amyloid and tau.
For more Health articles, visit www.foxnews.com/health
The hope is that this new timeline of how the illness impacts the mind will assist information the event of new treatments, based on researchers.
The examine was supported by the Nationwide Institute on Getting old and the NIH BRAIN Initiative.